1. Introduction to various parts of Zebra_GT800 barcode printer
1.1 Status indicator light/feed button/release latch/interface connector/folding media entry slot/DC power switch and socket
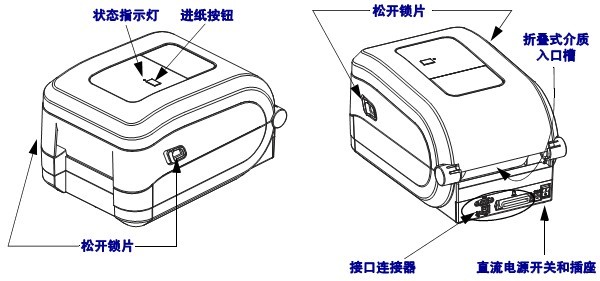
1.2 Ribbon roll hook supply shaft/pick-up shaft/web sensor/media guide gear adjuster/paper roll hook and media guide/black line sensor/elevation angle sensor/platen roller/print head/ribbon end sensor
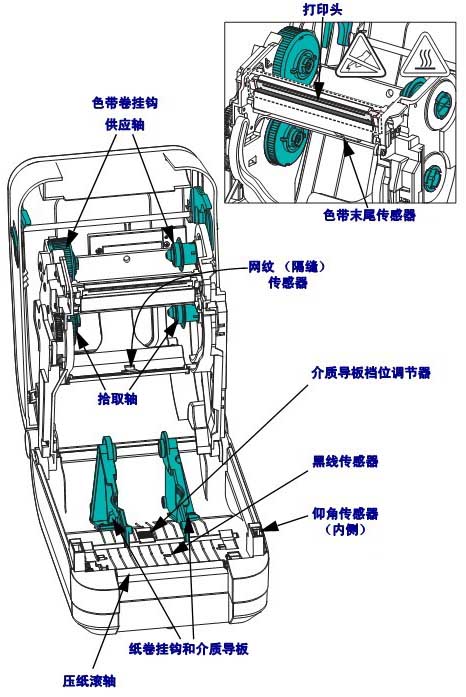

1.3 Power switch/color depth control switch
CAUTION: Turn off the printer before connecting or disconnecting communications and power cords
The Operator Color Depth Control switch allows the operator to modify color depth settings without changing the program or driver settings sent to the printer. This allows the user to adjust settings for small changes in the media and printer.
The control switch has three settings: low (1), medium (2), and high (3). The Low (1) setting does not change the actual Color Depth setting set through programming or driver settings. The Medium (2) setting increases the depth level by 3 stops; for example, if the printer is set to the default depth setting of 20, the actual color depth setting applied when printing will be 23. The “High (3)” setting adds 6 color depth levels to the color depth setting level.
Important: Setting the color depth to high or low will reduce the readability of the barcode.
2. Zebra GT800 barcode printer installation instructions
2.1 Load roll media
When loading media, rolls of media must be placed in the media supply bay and the correct media must be used for the type of printing required.
① Turn on the printer. Note that you need to pull the release button lever towards the front of the printer;
② Open the roll media hook, use your other hand to pull the media guide open, place the roll media on the paper roll hook, and release the guide plate. Adjust the position of the roll media so that the print side faces up when it passes over the printing roller;
③ Pull out the media so that the media protrudes from the front of the printer. Check whether the roll media can rotate freely. Do not put the roll media into the bottom of the media compartment. Check whether the printing side of the media is facing up;
④ Push the media under the two media guides;
⑤ If you do not need to install the thermal transfer ribbon, close the top cover;
2.2 Load the thermal transfer ribbon
The GT800 printer features a flexible ribbon system. It supports 300 meters and 74 meters of ribbon, and it also supports two ribbon roll adapters that can use 25.4 mm inner diameter ribbon rolls.
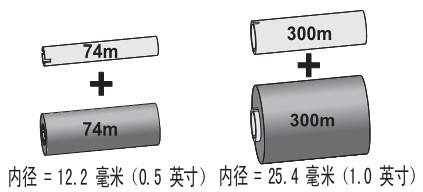
Requirements for thermal transfer ribbons:
● Media and ribbon types should match for best printing results
● To protect the print head from wear and tear, use a ribbon wider than the media.
● For thermal printing, do not install ribbon in the printer
● Use an empty ribbon roll that matches the inner diameter of the thermal transfer ribbon roll. Ribbon wrinkles or other printing failures may occur.
● Do not use ribbon rolls with damaged grooves, worn corners, broken, or shredded ribbon rolls. The grooves in the ribbon core should be intact so that the ribbon core can be fixed on the spindle. Otherwise, the ribbon core will slip, causing ribbon curling, ribbon end sensing errors, or other intermittent errors.
2.2.1 Load the standard core thermal transfer ribbon
Check whether there are gaps on both sides of the ribbon and empty ribbon core. If there are no gaps, please install them according to the non-standard core installation method.
① Open the printer cover and place the empty ribbon core on the printer pickup shaft. Push the right side of the empty ribbon core into the spring-pressed rotating shaft (right side), align the ribbon core with the center of the left rotating shaft hub, and rotate the ribbon core until the notch is aligned and locked.
② Place the new ribbon roll on the bottom ribbon supply shaft of the printer, push it into the right shaft, and lock the left side. The operation method is the same as fixing the pickup ribbon core.
③ Connect the ribbon to the pickup ribbon core, use the tape on the new pickup shaft, or use a piece of thin tape, align the ribbon, and let it wrap straight around the ribbon core.
④ Rotate the ribbon pick-up hub backward at the top to tighten the slack of the ribbon. The rotating hub helps to accurately align the ribbon pick-up position with the ribbon supply axis, and the ribbon leader should be completely covered by the ribbon.
⑤ Check that the media has been loaded and is ready to print, then close the printer cover.
⑥ When the printer is powered on, press the “Feed” button, let the printer feed a section of media of at least 20cm, tighten the slack part and ribbon wrinkles, make the ribbon straight, and align the ribbon on the rotating shaft.
⑦ Change the print mode setting from thermal to thermal transfer to set the printer temperature profile for thermal transfer media. This setting can be done through the printer driver, application software, or printer programming commands.
2.2.2 Load non-standard core thermal transfer ribbon
Loading non-standard core ribbon into the printer requires the use of a Zebra ribbon core adapter.
When using ribbons with non-standard cores for printers, at least the following requirements should be met:
● The inner diameter of the ribbon core should be 25.4mm. Material: Hard materials such as fiberboard and plastic core may not work properly.
● Ribbon width range: 110 to 33 mm.
● The maximum outer diameter of the ribbon is 66mm.
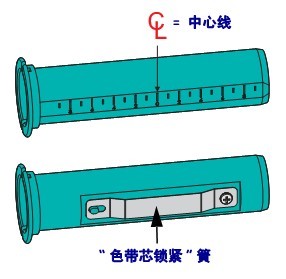
Adapters center the ribbon and ribbon core onto the media and printer. The adapter has a “ribbon core lock” spring that secures the soft fiberboard on the inside of the ribbon core and serves as a ruler to measure from the centerline of the printer when loaded into the printer.
① Load an empty ribbon core into the ribbon core adapter. The empty ribbon core should be the same as or slightly larger than the width of the ribbon roll. Place the center of the ribbon core roughly on top of the center line of the adapter. You can use an empty standard ribbon core without using an adapter and an empty non-standard ribbon core. The printer comes with a 300 meter empty ribbon core.
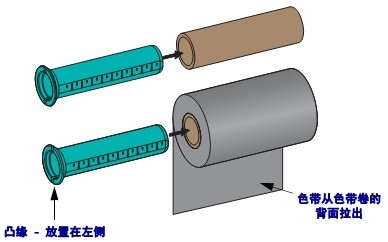
② Load the non-standard ribbon roll into the ribbon core adapter, align the adapter flange to the left, and check whether the ribbon unfolds the back of the ribbon roll as shown. Place the center of the ribbon core roughly on top of the centerline of the adapter.
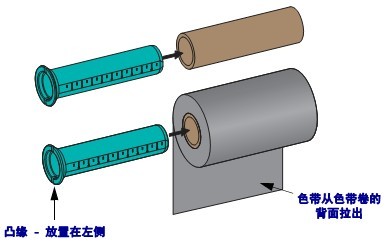
The 110mm maximum width media roll does not need to be centered. For media smaller than the maximum width and up to the minimum width of 33mm, the graduated scale on the adapter core should be used to align the ribbon roll with the media and printer.
③ Place the adapter with the empty ribbon core on the pickup spindle, and place the adapter with the ribbon roll on the bottom supply spindle. The right side of the ribbon core adapter mounts to the tapered end of the spring-loaded right side spindle. Push the adapter further onto the right side of the spindle and install the adapter onto the left hand wheel hub. Rotate the adapter and hub until the grooves on the adapter flange align and lock onto the spokes of the left spindle hub.
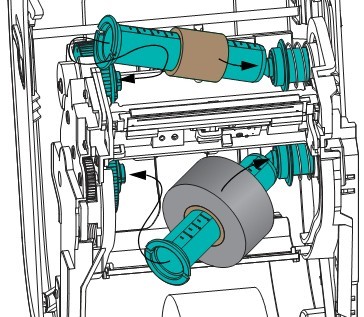
④ During the installation of the ribbon and empty ribbon core in the previous step, they may deviate from the center position. Check whether the ribbon roll and empty ribbon core are aligned with the center of the media (labels, paper, etc.). Note: You can use the centerline ruler on the ribbon core adapter to adjust the position.
If you forgot to check that the ribbon is wide enough for the media, you can still check now. To protect the print head, the ribbon must be wider than the media (including the label liner or backing).
⑤ Connect the ribbon to the pickup ribbon core. Use a thin piece of tape to secure the ribbon to the pickup core, aligning the ribbon so it wraps straight around the core.
⑥ Rotate the ribbon pickup hub backwards from the top to tighten the slack part of the ribbon. Rotating the hub can help accurately align the ribbon pickup position with the ribbon supply axis. The ribbon should be wound around the ribbon pick-up core at least one and a half times.
⑦ Check that the media is loaded and ready to print, then close the printer cover.
⑧ When the printer is powered on, press the “Feed” button, let the printer feed a section of media of at least 20cm, tighten the slack part and the ribbon wrinkles, make the ribbon straight, and align the ribbon on the rotating shaft.
⑨ Change the print mode setting from thermal to thermal transfer to set the printer temperature profile for thermal transfer media. This setting can be done through the printer driver, application software, or printer programming commands.
2.3 Print test (printer configuration) label
Before connecting the printer to the computer, make sure the printer is in normal working order. You can print a configuration status label to confirm.
① Make sure the media is installed correctly and the top cover of the printer is closed. If the printer is not already powered on, power it on. If the printer status indicator light flashes green during the initialization process (pause state), you should press the “Feed” button to set the printer in “Ready” mode. If the printer status indicator light does not turn solid green, please refer to the subsequent troubleshooting.
② Press the “Feed” button two to three times to let the printer perform calibration according to the loaded media. During this process, the printer may feed multiple labels.
③ When the status indicator light remains green, press and hold the “Feed” button until the status indicator light flashes once.
④ Release the “Feed” button. A configuration label will print out.
2.4 Pre-install Windows printer driver
Zebra has changed the installation method to use the printer through the Windows operating system based on the PC system. It is recommended to pre-install at least the ZebraDesigner Windows driver to take advantage of its simplicity and ease of use, as well as the convenience of the Windows operating system after Windows XP SP2 version.
Zebra provides Zebra Setup Utilities (ZSU), which is a set of Zebra printer drivers, utilities, and communication and installation tools that can be used for most Windows PC operating systems. Zebra Setup Utilities and Zebra windows printer drivers can be obtained from the user CD, or the latest version can be obtained from the Minyong website (www.chongshang.com.cn).
ZebraDesugber driver and Zebra Setup Utilities (including driver): Support Windows7, Windows Vista, Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows Server2008 and Windows Server2003 operating systems. The driver supports 32-bit and 64-bit Windows operating systems and has been certified by Microsoft. The ZebraDesugber driver and Zebra Setup Utilities support the following printer communication interfaces: USB, parallel, serial, wired and wireless Ethernet, and Bluetooth (using the Bluetooth virtual printer port).
Zebra Setup Utilities should be installed first before powering up the printer connected to the PC. Zebra Setup Utilities will prompt you to power up the printer. Continue with the following steps to complete the printer installation.
2.4.1 Plug and Play (PnP) printer detection and Windows operating system
Newer Windows operating systems can automatically detect the printer when it is connected via the USB interface. Depending on the hardware configuration and Windows version, printers can be detected via plug-and-play when connected to USB, parallel, and serial ports. The printer driver currently does not support serial port plug-and-play installation. The printer’s serial port PC interface configuration must support and have two-way communication capabilities to achieve plug-and-play. The first time you connect a printer to your PC, the operating system will automatically launch the Add New Hardware wizard, and if the Zebra Setup Utility comes with a preinstalled driver suite, the printer driver will automatically be installed. Go to the Windows printer directory, right-click the mouse, select “Properties”, click the “Print Test Page” button to verify whether the installation is successful.
If you reconnect the printer to the USB port or power on the printer after the PC completes the reboot of the operating system, the Windows operating system will detect and reconnect the previously installed printer. Ignore the warning that a new device has been detected and close the taskbar prompt. After waiting a few seconds for the operating system and driver software to match, the warning message will exit and the printer is now ready to print.
2.4.2 Universal Serial Bus (USB) device communication
When using the USB interface, the printer is the terminal device (not the host or hub).
NOTE: A scanner, scale, or other data input (terminal) device must use a serial port (not a USB port) to send data to the printer.
2.4.3 Serial Ports and Windows Operating Systems
In addition to the data flow control settings, the default settings for the serial port communication of the Windows operating system match the default settings of the printer. The default data flow control setting of Windows is NONE. The GT800 printer needs to set the data flow control setting to Hardware.
Note: GT800 printers currently do not support plug-and-play device detection for Windows serial ports.
2.4.4 Ethernet
The GT800 printer options feature multiple methods and applications to help connect the printer to a network (WAN or LAN) and configure wired and wireless (Wi-Fi) printers. The Zebra Setup Utility configuration wizard supports printers using IP addresses to connect to printers on shared networks through Windows-based systems. The printer has an internal web page that makes it easy to configure the printer and network. This web page can be accessed using a web browser through the printer’s IP address. The free version of ZebraNet Bridge software allows users to centrally deploy, manage and monitor Zebra printers. Zebra’s printer auto-discovery feature can discover up to 3 printers from a preset PC screen anywhere on the global network. ZebraNet Bridge Enterprise can be purchased to manage large numbers of Zebra printers.
2.5 Connect the printer to the computer
The Zebra GT800 printer supports a variety of interface options and configurations. These include: Universal Serial Bus (USB) interface, RS232 serial interface, parallel interface (IEEE1284) and 10/100 Ethernet.
CAUTION: When connecting the interface cable, place the power switch in the off position. Before connecting or disconnecting communications cables, the power cord must be plugged into the power supply unit and the electrical outlet on the back of the printer.
Interface cable requirements:
Data cables must be of fully shielded construction and equipped with metal or metallized connector housings. To prevent radiated and received electrical noise, shielded cables and connectors must be used.
To minimize the level of electrical noise pickup in cables, do the following:
● Data cables should be as short as possible (1.83m long cable is recommended)
● Do not bundle data cables and power cords tightly together
● Do not tie data cables to power conduits
2.6 After connecting the printer
You can now establish basic communication with the printer and test printer communication, and then install other printer-related applications, drivers, or utilities.
Verifying the operation of the printing system is a relatively simple task. For Windows operating systems, the Zebra Setup Utility or the Windows “Printers and Faxes” control panel can operate and print a test label. For non-Windows operating systems, a (~WC) command can be used to copy a basic ASCII text file to print a configuration status label.
2.6.1 Test printing using Zebra Setup Utility
① Open Zebra Setup Utility
② Click the icon of the newly installed printer, select the printer and enable the printer configuration button under the printer in the window.
③ Click the “Open Printer Tools” button.
④ In the “Print” tab window, click the “Print configuration label” line and click the “Send” button. The printer will print the configuration status label.
2.6.2 Use the Windows “Printers and Faxes” menu to test the printing situation
① Click the Windows “Start” menu button and go to “Printers and Faxes”, or go to the “Control Panel” “Printers and Faxes” menu to open the menu.
② Select the newly installed printer icon, select the printer, and right-click the mouse to open the printer’s “Properties” menu.
③ From the printer’s “General” tab window, click the “Print Test Page” button, and the printer will print the Windows test print page.
2.6.3 Perform a test print to an Ethernet printer connected to the network (LAN or WAN) using the MS-DOS command prompt or from the Windows XP Start menu
① Create a text file using three ASCII characters: ~WC
② Save the file as: TEST.ZPL (any file name and extension)
③ Read the IP address on the network status printout of the printer configuration status label. While connected to the same LAN or WAN as the printer, type the following into the address bar of the web browser window and enter: ftp 123.45.67.01 (assuming the IP address is 123.45.67.01)
④ Type the file name, then enter “put” and press Enter. For this “test print” file it should be: put TEST.ZPL
2.6.4 For non-Windows operating systems, use copying the ZPL command file to perform test printing
① Create a text file using three ASCII characters: ~WC
② Save the file as: TEST.ZPL (any file name and extension)
③ Copy the file to the printer. For DOS environment, send the file to the printer connected to the system parallel port. The command is very simple: COPY TEST.ZPL LPT1
3. Zebra GT800 barcode printer printing operation
3.1 The printer is not operated or stored for a long time
A printhead that has been stored for a long time may stick to the platen roller. To avoid this, store the printer with a piece of media (label or paper) between the printhead and the platen roller. Do not ship the printer with a media roll installed, otherwise the printer or media may be damaged.
3.2 Printing mode
The GT800 printer works in different modes and various media configurations:
● Thermal printing (this method uses heat-sensitive media for printing)
● Thermal transfer printing (this method uses a ribbon to print on the media using the principle of thermal transfer)
● Standard tear-off mode allows users to tear off labels (or batch-printed label strips) after printing each label
● Label peeling mode: If a label peeler is installed, the label can be peeled off from the backing material during the printing process. After removing this label, the next label can be printed immediately.
● Stand-alone mode: The printer can print without being connected to a computer serial port when using the auto-run label function (according to programming) or using a data input device connected to the printer’s parallel port. In this mode, you can use data entry devices such as scanners, scales, Zebra KDU Plus, or Zebra KDU (Keyboard Display Unit).
● Network shared printing: Printers equipped with the Ethernet interface option have a built-in print server that can manage and monitor the status of Zebra printers on the network through the ZebraLink printer configuration web page and ZebraNet Bridge software.
3.3 Types of printing media
Important: For uninterrupted high-quality printing, Minyong strongly recommends the use of Minyong recommended consumables. A variety of specially designed papers, polyethylene, polyester and vinyl products can improve the printing performance of the printer and prevent premature wear of the print head.
The GT800 printer can use a variety of media types:
● Standard Media – Most label non-continuous media use an adhesive material that allows multiple individual labels or a length of continuous labels to be adhered to a backing.
● Continuous roll media – Most continuous roll media are thermal (similar to fax paper) and are suitable for receipt or ticket printing.
● Unbacked media – Unbacked labels have an adhesive material, but are wrapped around a core of media without a backing. The media is usually pre-punched and may also have black mark markings on the underlying surface of the media to indicate where the labels are separated. The top layer of labels on unbacked media has a special coating that prevents labels from sticking to each other. The printer must be equipped with a special “linerless” option to use linerless media and ensure that the media does not stick to the printer.
● Label Material – Labels are typically made from thick paper (up to 0.19mm thick), the label material has no adhesive or backing, and usually comes with pre-punched holes between each label.
① Non-continuous roll media
Roll media can be wound on core diameters from 12.7 to 38.1 mm. Labels have an adhesive backing that bonds the labels to the lining, and the labels are separated by spacers, notches, cut-out holes, or black marks. Labels are separated by perforations. Individual labels are separated by one or more of the following methods:
◆The textured media is separated by spacers, cut holes or notches.
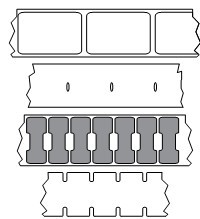
◆Black mark media uses pre-printed black marks on the back of the media to show label separation locations.
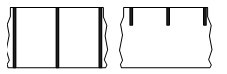
◆Pre-punched media has perforations that allow easy separation between labels or label materials. The media may also have black marks or other separation between labels.
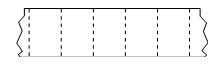
② Intermittent folded media, folded media folded in a staggered manner, folded media can have the same separation method as the intermittent media roll. The separation location may be at or near the fold.
③ Continuous roll media, roll media can be wound on a paper core with a diameter of 12.7 to 38.1 mm. Continuous rolls of media have no gaps, cutouts, notches, or black marks to indicate where labels are separated. Images can be printed anywhere on the label, and individual labels can be cut with a cutter. If using continuous media, a transmissive (gap) sensor should be used so that the printer can detect the media being ejected.
3.4 Adjust printing width
The print width must be set when:
● Using the printer for the first time
● Media width changed
You can set the print width in the following ways:
◆ Windows printer driver or application software such as ZebraDesigner.
◆ With the printer power on and the top cover closed, press and hold the “Feed” button for a few seconds. The green status indicator light will flash 5 times and then release the button. The printer will adjust the width. Starting from the minimum printing width to the maximum printing width of the printer, a frame will be printed continuously every 4mm. When the printer reaches the required maximum printing width, press the “Feed” button. Note: Printer drivers and applications may override this setting.
◆ Use ZPL programming to control printer operation, please refer to the “Print Width Command” (~PW) command.
◆ To control printer operation through “EPL page mode” programming, please refer to the “Set Label Width” (q) command.
3.5 Adjust print quality
Print quality is affected by printhead temperature or density settings, print speed, and the type of media used, experiment with these settings to find the best combination for your application. Print quality can be set using the Zebra Setup Utility’s “Configure Print Quality” program.
You can control the relative color depth (or density) setting in the following ways:
◆ With the printer power on and the top cover closed, press and hold the “Feed” button for a few seconds. The green status indicator light will flash 6 times and then release the button. The printer will adjust the depth, starting from the minimum color depth (printing density/heat) and ending at the printer’s maximum color depth. Use the ZPL depth setting range value to print a continuous bar code simulation pattern in increments of 4. If the pattern is clear and valid, press the “Feed” button. Do not continue to increase the color depth setting or the width of the barcode lines may be distorted, resulting in reduced readability. NOTE: Printer drivers and applications may override this setting.
It will override any color depth/density settings programmed via ZPL or EPL.
◆ (~SD) ZPL command for “set color depth”.
◆ “Color Depth” (D) ELP command.
If you find you need to adjust the print speed, you can use:
◆ Windows printer driver or application software such as ZebraDesigner.
◆ “Print Speed” (~PR) command.
◆ “Speed Select” (S) command.
3.6 Media sensing
The printer has automatic media sensing, and the printer is designed to continuously check and adjust media length sensing to accommodate subtle changes. As printing begins or media is fed, the printer continuously checks and adjusts media sensing to accommodate subtle changes in media parameters from label to label and from roll to roll within the same roll. When starting a print job or feeding media, the printer automatically initiates media length calibration if the expected media length or spacing between labels falls outside the acceptable variation range. The automatic media sensing feature in the GT800 printer is also suitable for printer operation using EPL and ZPL label formats and programming.
If the printer does not detect a label or black line (or notch with black line sensing) after feeding the media at the default maximum label length of 1 meter, the printer will switch to continuous media mode and will retain these settings if not changed using software or programmatically or manually calibrated for different media.
You can also choose to set the printer to perform a brief media calibration after the printer is powered on, or when printing is turned off while the power is on. During the calibration process, the printer will feed multiple labels.
You can verify the printer’s media settings by printing the Printer Configuration label.
You can use the “ZPL Maximum Label Length Command” (~ML) to reduce the maximum distance to be checked by the media type automatic detection and sensing process. It is recommended to set this distance to no more than twice the longest label to be printed. If the maximum size label to be printed is 4*6 inches, you can reduce the detection distance of the maximum label length from the default distance of 39 inches to 12 inches.
If the printer is unable to automatically detect media type and calibrate automatically, perform a full calibration, which includes a printed pattern of sensor operation for the user media. This method disables the printer’s auto-media sensing feature until the printer’s default parameters are reset to factory defaults using the four-flash feed button pattern.
The media automatic calibration function can be modified, turned on or off according to user needs. Print jobs sometimes require the printer to use an entire roll of media. You can use the “ZPL media feed command” (~MF) to independently control the two media automatic feeding situations (power on when loading media, or close the printer cover when power on). The feed operations discussed in the ZPL Programmer’s Guide for the ~MF command apply primarily to media autosensing and calibration. Automatic media calibration operations for controlling media (label-to-label) calibration can be implemented using the ~XS command. These settings should not be changed if multiple media types of different lengths, materials, and detection methods (web/gap, black line, notch, or continuous) are used.
The media calibration and detection process can also be refined to match the media type loaded into the printer, which can be set using the “ZPL Media Tracking” command (~MN). Printers sometimes detect preprinted media as spaces between labels, or backings with printed content as black marks, and if the ~MN parameter is set for continuous media, no automatic calibration is performed during printing. The ~MN command also includes an autocalibration parameter (~MNA) that can be used to return the printer to its default settings for automatic detection of all media types.
3.7 Fonts and Printers
The GT800 printer meets your language and font requirements with a variety of internal fonts, onboard font scaling, international font sets and code page support, Unicode support, and font download options.
The font function of GT800 printer is related to the programming language. The EPL programming language provides support for basic bitmap fonts and international code page fonts. The ZPL programming language provides advanced font mapping and scaling technology, supporting outline fonts (TrueType or OpenType) and Unicode font mapping, as well as basic bitmap fonts and character code pages.
The GT800 printer features a variety of tools and application software that support downloading fonts to the printer for both printer programming languages.
The GT800 printer has resident prefixes for supporting Simplified or Traditional Chinese.
3.7.1 Printer localization through code pages
The GT800 printer supports two major programming languages, ZPL and EPL. Each programming language has a set of font sets to support regions, countries and character sets. The printer supports localization using commonly used international character mapping code pages, as well as configuration status printout.
●For zpl code page support including Unicode, see the ^CI command in the ZPL Programmer’s Guide.
●For the ZPL configuration status printout language, please refer to the ^KL command in the “ZPL Programmer’s Guide”.
●For EPL code page support, see I Commands in the EPL Programmer’s Guide.
3.7.2 Identify fonts in the printer
Fonts and memory can be shared through the programming language in the printer. Fonts can be loaded into multiple memory areas in the GT800 printer, and ZPL programming technology recognizes both EPL and ZPL fonts. EPL programming technology can only recognize EPL fonts.
ZPL font:
● Fonts suitable for ZPL printer operation can be managed and downloaded using Zebra Setup Utility or ZebraNet Bridge.
● To display all fonts loaded into your printer, send the ZPL ~WD command to the printer.
The .FNT file extension in the ZPL language is used to identify bitmap fonts in different printer memory areas.
The .TTF, .TTE, or .OTF file extension in the ZPL language is used to identify scalable fonts. EPL does not support these fonts.
EPL font:
● To download fonts for EPL printing, use the Zebra Setup Utility or ZebraNet Bridge to send the file to the printer.
● To display soft fonts (ext.) available for EPL, the EPL command EI should be sent to the printer.
All EPL fonts displayed are bitmap fonts and do not include the .FNT file extension or horizontal and vertical indicators displayed using the ZPL command ^WD in the above ZPL fonts.
● To delete non-Asian EPL fonts through EPL programming, use the EK command.
● To remove EPL Asian fonts from the printer, use the ZPL ^ID command.
3.8 Independent printing
The printer can be configured to work independently without being connected to a computer. The GT800 printer can automatically run a single label printing format. One or more downloaded tag formats can be accessed using a terminal device, embedded device, or Zebra KDU (keyboard display unit) to use the tag formats. These methods allow developers to integrate data input devices such as scanners or scales into printers through the serial port.
Label formats developed can be stored in the printer to support labels with the following characteristics:
● No data input is required, just press the “Feed” button to print.
● No data entry required, prints when labels are removed from the printer’s optional label peeler.
● One or more data variables can be entered through a terminal or embedded device. The label will be printed after the last variable data field is entered.
● One or more label formats invoked by scanning a barcode that contains programming information for the running label format.
● A label format designed as a step in the process, where each label includes a barcode that contains programming information to run the next label in the process.
Both printer programming languages support special label formats that run automatically after a power cycle or reset. ZPL looks for a file named AUTOEXEC.ZPL, and EPL looks for a label format named AUTOFR. If both files are loaded into the printer, only AUTOEXEC.ZPL is run. If EPL AUTOFR is not disabled, it will always run. Both files must be deleted from the printer and then a reset or power cycle performed to completely delete the files.
3.9 Print counter
The GT800 printer is able to report maintenance alerts for the printhead, the printer can provide a cleaning function, and can provide advance warning when a calculated printhead life alarm arrives. If an RTC (Real Time Clock) is installed in the printer, date information can also be included in the printhead life and history reports. By default, print count alerts are disabled.
Multiple print counter messages and reports can be customized. To enable print counter alerts, send the following command to the printer:
● EPL command oLY
● ZPL command^JH,,,,,E
4. Zebra GT800 barcode printer maintenance
4.1 Clean the print head
Caution: The print head will become hot during the printing process. To prevent damage to the print head and personal injury, please do not touch the print head. Only use a cleaning pen or alcohol cotton for maintenance.
① Rub the cleaning pen on the black area of the print head and clean from the middle to the outside. This can clean the sticky substance transferred from the edge of the media to the outside of the print head along the media path.
② Wait for one minute before closing the printer cover.
4.2 Media path considerations
Use a cleaning swab to remove accumulated debris, dust, and dirt from hooks, guides, and media path surfaces.
① The alcohol in the cleaning swab soaks these particles to make them lose their stickiness.
② Wipe the protruding piece to remove accumulated debris.
③ Wipe the inner edges of the two media guides and the media holder to remove accumulated dirt.
④ Clean the back of the ribbon cover (movable baffle) and turn the cover down to a position where the top cover of the media can contact this surface. Adhesive on the edges of the label media may slowly stain and accumulate on the inside surface.
⑤ Wait for one minute before closing the printer cover and discard the used cleaning swab.
4.3 Sensor cleaning
Dust can accumulate on the media sensor.
① Use a brush to gently brush off the dust, or use a compressed air can to blow off the dust. Do not use an air compressor – oil and sewage in the air pump will stain the printer and print head. Use dry cotton swabs to wipe away dust as needed. If there is still glue or other dirt, you can use alcohol to moisten the cleaning swab to remove it.
② Use a dry cleaning swab to remove any remaining dirt after the first cleaning.
③ Repeat steps 1 and 2 as needed until all residue and traces of dirt are removed from the sensor.
4.4 Cleaning and replacing the printing roller
The label printing roller (drive roller) generally does not require cleaning, and although paper dust and backing debris may accumulate, it will not affect the printing operation. Dirt on the print roller will damage the print head and cause the media to slip or stick during printing. Glue, dirt, dust, oil and other dirt should be removed from the print roller immediately.
If printer performance, print quality, and media handling are significantly reduced, the print roller (and media path) should be cleaned. The platen roller is the printing surface and the driving wheel for the media. If sticking or paper jams still occur after cleaning, the platen roller must be replaced.
You can use a fiber-free cleaning swab or a lint-free cloth moistened with a little alcohol to clean the print roller.
① Print cover and remove the media from the print roller area.
② Pull the left or right print roller bearing lock release tab toward the front of the printer and rotate it upward.
Note: The support arm of the print roller has a complicated structure. Move the support arm outside the printer to clean the grooves on the bearing seat. Then, slowly and gently pull the support arm toward the front of the printer to remove the print roller. Be careful when installing the bearings.
③ Take out the printing roller from the bottom bracket of the printer.
④ Use a cleaning swab moistened with alcohol to clean the printing roller from the center to the outside. Repeat this process until all platen roller surfaces are clean. If you find that there is a lot of accumulated sticky matter or serious label blockage, you should use a new cleaning swab to repeat the operation to remove residual dirt. The first cleaning can dilute the sticky matter and oil stains, but it may not be completely removed.
⑤ Install the printing roller into the printer. The cleaning swab cannot be reused and should be discarded after use.
⑥ Make sure that the bearing and drive gear are located on the printing roller shaft.
⑦ Align the printing roller and gear to the left, and put them downward into the bottom bracket of the printer.
⑧ Gently turn the locking pin of the print roller bearing downward toward the rear of the printer to release the tab, and lock it into the notches on both sides of the bearing groove.
The printer should be allowed to dry for about a minute before closing the media cover.
4.5 Replace the print head
CAUTION: Prepare your work area to prevent electrostatic discharge, anti-static measures must be taken in the work area, support the printer with a properly grounded conductive shock pad, and the operator themselves should wear a conductive wrist strap.
CAUTION: Turn off the printer and unplug the power cord before replacing the printhead.
4.5.1 Print head removal
① Turn on the printer. Remove the thermal transfer ribbon from the printer.
② Grasp the right side of the print head cover bracket and gently pull the bracket off the print head. There is a gap on the side of the cover for your thumb to grab. You can use other fingers to provide more force to pry the cover from the ribbon bracket.
③ Use the short guide arm on the left side of the print head cover to release the print head from the ribbon holder.
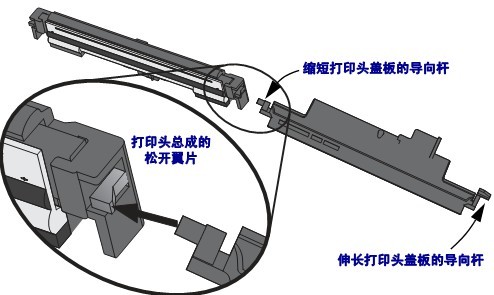
Push the shortened guide rod to the right side of the ribbon holder and press the printhead release tab.
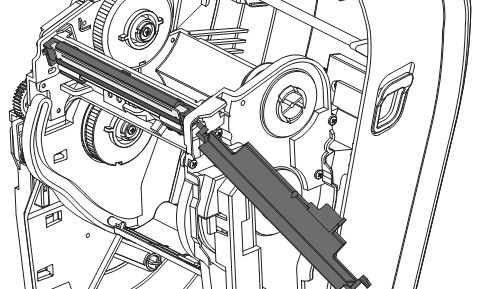
If necessary, push the shortened guide rod to the left side of the ribbon holder and press the other release tabs of the printhead.
④ Use a cross-head screwdriver to remove the screw securing the ground wire (green).
Gently and slowly pull the two printhead cables straight out of the connectors to disconnect the cables from the printhead assembly. Pulling the connectors out at an angle can damage the printhead’s connector pins and sockets.
4.5.2 Reinstallation of print head
Reverse the print head removal steps to reinstall the print head.
① Connect the two print head cables to the print head.
② Connect the ground wire to the print head assembly.
③ Insert the center pivot tab of the print head assembly into the groove of the ribbon holder.
④ Lock the left and right sides of the print head assembly into the ribbon holder, and check whether the print head is correctly fixed by the locking tabs and the bracket. You can also press both sides of the print head toward the ribbon holder again to check whether the tabs are correctly fixed.
⑤ Check that the print head can move freely up and down when pressure is applied, and remains in the locked position when released.
⑥ Clean the print head.
⑦ Reload the media. Plug in the power cord, turn on the printer, and print a status report to make sure the printer is working properly.
5. Troubleshooting for Zebra GT800 barcode printer
This section provides printer failure reporting information that you may need to perform printer troubleshooting procedures. It also includes various diagnostic tests.
5.1 Status indicator light description
| Indicator light status and color | Printer status | See numbers below for workarounds |
|---|---|---|
| go out | closure | 1 |
| Stay green | Open | 2 |
| Lasts amber | Stopped | 3 |
| flashing green | Stopped | 4 |
| Flashing red | Stopped | 5 |
| red double flash | Suspended | 6 |
| amber flashing | Suspended | 7 |
| Flashing red and green alternately | Need repair | 8 |
| Flashing red, flashing red and green | Requires repair or restart | 9 |
| Blinking red, amber and green (do not reset or power off) | Memory card defragmentation | 10 |
5.2 Solutions to status indicator light errors
The following status error indicator solution numbers correspond to the “Status Indicator Description” table in 5.1. Each error number has one or more workarounds for troubleshooting the listed error.
1. The printer is not powered on
● Is the printer powered on? ● Check the power connections from the wall outlet to the power supply and from the power supply to the printer.
● Disconnect the printer from the wall outlet for 30 seconds, and then reconnect the printer to the wall outlet.
2. The printer is powered on and in standby mode.
No action is necessary.
3. The printer failed the power-on self-test (POST).
● If the error occurs when turning on the printer, please contact Digital for assistance. If the printer is working properly, the printer status light lights amber for 10 seconds before turning green (solid or blinking).
A memory error has occurred.
● If the error occurs after printing is complete, turn the printer off and on again, then resume printing.
Need to let the print head cool
● If this error still occurs, turn off the printer, wait for at least five minutes, and then turn it back on. If the amber light is still on, the printer needs service.
4. The printer is receiving data
● After receiving all data, the status indicator light will turn green and the printer will automatically resume operation.
5. The media is used up.
● Reload the roll media and press the Feed button to resume printing.
Ribbon ran out
● The printer has detected the end of the ribbon roll. Replace the ribbon.
Print head open
● Close the top cover and press the Feed button to resume printing.
6. The printer pauses.
● Press the “Feed” button to restart printing.
7. The print head temperature is too high.
● Printing will be paused, waiting for the print head to cool down to an acceptable printing temperature. Once this temperature is reached, the printer will automatically resume work.
8. The flash memory is not programmed.
● Return the printer to the point of purchase.
9. A serious failure occurs in the print head or motor.
● Return the printer to the point of purchase.
● The print head may have a “THERMAL SHUTDOWN” error. Turn the printer off, let the printer cool down for a few minutes, and then turn the power back on. If the error still occurs, the printer should be sent to Sensitive Digital.
10. The printer is defragmenting the memory.
CAUTION: Do not turn off the printer during defragmentation, as this may damage the printer.
● Defragmentation is a daily operation of the printer. Performing this operation can better manage the space usage of the memory card. The printer will defragment the memory card when factory defaults are restored and the printer detects that defragmentation is required.
When the printer is in this state, the printer should be allowed to complete defragmentation. If warnings are issued frequently, please check the label format. Frequent writing or erasing formats from memory may cause the printer to defragment frequently. The need for defragmentation can be minimized by using a format that avoids frequent rewriting of memory.
● If the warning condition does not go away, contact Technical Support. The printer needs repair.
5.3 Print quality issues
5.3.1 Nothing is printed on the label.
① In the case of printing without ribbon, the media may not be thermal media.
② For thermal transfer printers, the media cannot have winding problems, nor can mismatched printer ribbons be used.
③ Has the media been loaded correctly?
5.3.2 The printed image is incorrect
① The print head is dirty, clean the print head.
② The print head temperature is too low.
③ Adjust the print depth and/or print speed.
④ The media being used is incompatible with the printer.
⑤ The print head is worn. The print head is a consumable part and will wear out due to the friction between the media and the print head. Using substandard media may shorten the life of the printhead or damage the printhead. Replace the print head.
⑥ The printing roller needs to be cleaned or replaced. The print roller may lose traction for the following reasons:
●There are foreign objects on the surface.
●The smooth surface of the rubber material has been changed to a polished and slippery effect.
●A generally smooth printing surface may be damaged like a folding knife cut.
5.3.3 There are many places on multiple labels with no printed content (blank vertical lines)
① The print head is dirty, clean the print head.
② The print head element is damaged.
5.3.4 The printing action does not start from the top of the label, or one to three labels have printing errors.
① The media is not correctly stringed.
② The printer needs calibration.
③ ZPL label format – the correct media sensor may not be enabled. Manual calibration allows you to select the media sensing method for the label to be used. (^MN command)
④ ZPL Label Format – Check that the “Label Top” (^LT) command is set correctly for your application.
⑤ EPL Label Format – For label delivery, black line or notch sensing, or gap/cut sensing, the correct media sensor may not activate. Manual calibration allows you to select the media sensing method for the label to be used. (o and Q commands)
⑥ EPL Label Format – Check that the “Set Label Length” (Q) command is set correctly for your application.
5.3.4 The ZPL label format has been sent to the printer, but the printer cannot recognize it.
① Is printing in pause mode? If so, press the “Feed” button.
② Check whether the data cable is installed correctly.
③ If a communication failure occurs, first, check whether the correct communication port on the computer has been selected.
④ Check whether the correct “Format” and “Control Prefix” on the printer match what is used in the ZPL programming label format. The default format is an up arrow (^) character, and the control character is a tilde (~) character.
5.3.5 The EPL label format has been sent to the printer, but the printer cannot recognize it.
① Is printing in pause mode? If so, press the “Feed” button.
② Check whether the data cable is installed correctly.
③ If a communication failure occurs, first, check whether the correct communication port on the computer has been selected.
④ If the printer has the label peel function enabled, the printer will wait for the user to remove the label, and the backing paper/web must be correctly fed through the label peeler to work correctly in label peel mode.
5.4 Manual calibration
Manual calibration is recommended if you are using preprinted media or if the printer does not automatically calibrate correctly.
① Make sure the media is loaded.
② Turn on the printer power.
③ Press and hold the “Feed” button until the green indicator light flashes once, then twice, and continues to flash until the flash combination reaches a set of seven flashes. Release the Feed button.
④ The printer will set up the media sensor for the label backing to be used. After this adjustment, the roll media will automatically feed until the label is positioned under the printhead, and a chart of the media sensor settings will print out. After the above operation is completed, the printer will save the new settings in memory and the printer will be ready for normal operation.
⑤ Press the “Feed” button to feed a whole blank label. If it does not feed, you should try returning the printer to defaults and performing a printer recalibration.
Note: Performing manual calibration disables the automatic calibration feature. To return to automatic calibration mode, restore the printer defaults.
5.5 Paper feed button mode
| power off mode | |
|---|---|
| When the printer is powered off, press and hold the “Feed” button when the printer is powered on. | |
| flash sequence | operate |
| Amber-red flashing | Firmware Download Mode – The printer begins flashing red rapidly, indicating that it has entered “Firmware Download” mode. At this point, release the “Feed” button to initialize the printer and start downloading. When the printer status light begins blinking slowly red and green, the printer is ready to begin downloading firmware. |
| amber | Normal operation mode – the printer enters the normal initialization process. At this time, releasing the “feed” button allows the printer to start normally without downloading firmware and work in communication diagnostic mode. |
| green | Communication Diagnostic Mode – Immediately after the printer status indicator turns green, release the “Feed” button, the printer will print “Now in DUMP” on the top of the label, and then advance to the next label. After printing the first label, the printer will automatically enter diagnostic mode, and the printer will print out a text representation of the subsequently received data in diagnostic mode. To exit diagnostic mode and resume printing, power the printer off and on again. Another way to exit diagnostic mode is to press the Feed button multiple times. This clears the printer’s command cache and prints “Out of DUMP” on the label. |
| Power on mode | |
|---|---|
| With the printer powered on and the top cover closed, press and hold the “Feed” button for a few seconds. The green indicator light will flash several times. The description on the right (Operation) shows what happens to the printer when the button is released after the light has flashed a specific number of times and before the next flash sequence begins. | |
| flash sequence | operate |
* | Configuration status – A detailed printer configuration status report can be printed. The label can be used to verify the printing effect, help the printer calculate the communication configuration, and perform maintenance, troubleshooting, and help users communicate with customer service. |
* ** | Standard Media Calibration – The printer detects and sets the media type and media length, which adjusts the media sensor for optimal performance for the loaded media (equal to ZPL command ~JC). The printer will feed one to four labels during the calibration process. |
* ** *** | Serial Port Configuration – Applies only to printers with a serial interface port. To reset the communication parameters for a serial port other than database control, press and release the Feed button while the light flashes amber and green rapidly. To synchronize the baud rate automatically: Send the ^XA^XZ command sequence to the printer while the light is flashing amber and green rapidly. When the printer and host are synchronized, the light switches to solid green. Note: Labels will not print during the automatic baud rate synchronization process. |
* ** *** **** | Factory Default – The printer can be reset to factory default settings (equal to ZPL command ~JUN). Some configuration setting values were not returned to the initial installation settings. Other setting values that are set, viewed, and controlled programmatically will also be reset. During the memory defragmentation process, the printer will perform a standard media calibration process. After the network printer enters factory default mode, the status light will turn amber within three seconds. During this process, the user can perform two actions: the printer will automatically reset to factory defaults as described above without performing any action, or the printer can enter factory default reset mode (equivalent to the ZPL command ^JUF) by holding down the “Feed” button when the network printer option is installed. Releasing the button after the first flash resets the network’s factory options (equivalent to the ZPL command ^JUN). Releasing the button after the second flash sequence (two flashes) only resets the printer defaults. After the third flash, release the button to reset the printer and network settings (ZPL commands ^JUN and ^JUF) |
* ** *** **** ***** | Printing width adjustment – from the minimum printing width to the maximum printing width of the printer, continuously print a frame every 4 mm. When the printer reaches the required maximum printing width, press the “Feed” button. Note that printer drivers and applications may override this setting. |
* ** *** **** ***** ****** | Print Depth (Density) Adjustment – Prints a continuous bar code simulated pattern in increments of four using the ZPL depth setting range value, starting from the minimum color depth (print density/heat) and ending at the printer’s maximum depth. If the pattern is clear and effective, press the Feed button and do not continue to increase the color depth setting, otherwise the width of the barcode lines may be distorted, resulting in reduced readability. Note that printer drivers and applications may override this setting. |
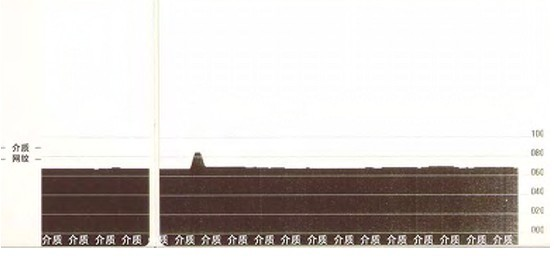
* ** *** **** ***** ****** ******* | Manual Media Calibration – The printer runs a comprehensive test to detect and set the media type and media length, which adjusts the media sensor for optimal performance for the installed media (equal to the ZPL~JG command). Manual calibration is recommended if you are using pre-printed media, if the printer does not automatically calibrate correctly it may print on the label backing. A graphical diagram of media sensing will be printed. |
| If the Feed button remains pressed after the 7 flash sequence, the printer will exit configuration mode when the user releases the Feed button. |
6. Zebra GT800 barcode printer ZPL configuration
6.1 ZPL printer configuration format
Create a printer configuration programming file and send it to one or more printers to manage multiple printers, or use ZebraNet Bridge to replicate printer settings. The following shows the basic structure of the ZPL programming configuration file:
^XA——Start format command
The order of format commands is very important
Ⅰ.General printing and command settings
Ⅱ.Media handling and operation
Ⅲ.Media printing size
^JUS save command
^XZ——End format command
Create programming files. Programming files can be sent to the printer using the Zebra Setup Utility (ZSU). Programming files can be created using Windows Notepad (text editor).
6.2 Reference for comparing ZPL configuration status and commands
| Order | List name | illustrate |
|---|---|---|
| ~SD | DARKNESS | Default: 10.0 |
| – | DARKNESS SWITCH | not applicable |
| ^PR | PRINT SPEED | Default: 6IPS/152.4mm/sec (maximum) |
| ~TA | TEAR OFF | Default value: +000 |
| ^MN | MEDIA TYPE | Default value: GAP/NOTCH (gap/cut) |
| SENSOR TYPE | Default value: WEB (texture) | |
| SENSOR SELECT | Default: AUTO (^MNA – auto-detect) | |
| ^MT | PRINT METHOD | THERMAL-TRANS (thermal transfer) or DIRECT-THERMAL (thermal) |
| ^PW | PRINT WIDTH | Default: 832 points |
| ^LL | LABEL LENGTH | Default value: 1225 points (value calibrated in time by automatic web-gap detection for label media) |
| ^ML | MAXIMUM LENGTH | Default value: 39.0IN 989MM |
| – | USB COMM. | Connection status: connected/not connected |
| – | PARALLEL COMM. | Available connections: BIDIRECTIONAL (bidirectional) |
| ^SCa | BAUD | Default value: 9600 |
| ^SC,b | DATA BITS | Default: 8BITS (8 bits) |
| ^SC,,C | PARITY | Default value: NONE |
| ^SC,,,,e | HOST HANDSHAKE | Default: DTR or XON/XOFF |
| ^MFa | MEDIA POWER UP | Default: NO MOTION |
| ^MF, b | HEAD CLOSE | Default: FEED |
| ~JS | BACKFEED | Default value: DEFAULT |
| ^LT | LABEL TOP | Default value: +000 |
| ^LS | LEFT POSITION | Default value: +0000 |